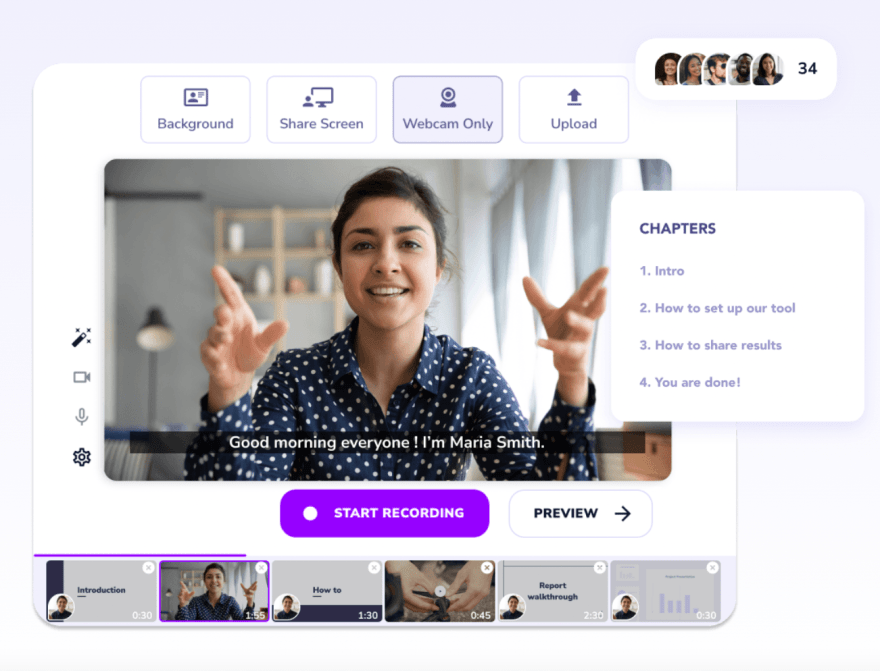
Interactive content for training is revolutionizing the way we learn and develop skills. Gone are the days of passive lectures and monotonous textbooks. Today, learners engage with interactive exercises, simulations, and games that make learning both effective and enjoyable.
This approach leverages the power of active participation to foster deeper understanding, enhance knowledge retention, and ultimately, lead to improved performance. By tapping into various learning styles and preferences, interactive content caters to individual needs, making learning a more personalized and engaging experience.
Defining Interactive Content
Interactive content is a vital component of modern training programs, offering a dynamic and engaging learning experience that goes beyond traditional methods. It allows learners to actively participate in the learning process, making it more effective and memorable.
Interactive content is a powerful tool for training, engaging learners through hands-on experiences and personalized feedback. This approach can be particularly effective when combined with emerging technologies like voice search. By optimizing your training materials for voice search, you can create a more intuitive and accessible learning experience.
For instance, you could integrate voice commands to guide learners through simulations or allow them to ask questions verbally. For a comprehensive guide on voice search optimization, check out this resource on Voice search optimization for mobile app development.
By incorporating these strategies, you can create interactive training content that is both engaging and accessible.
Characteristics of Interactive Content
Interactive content is characterized by its ability to engage learners through active participation and feedback. Here are some key characteristics:
- Active Participation:Learners are not passive recipients of information but actively engage with the content through tasks, simulations, quizzes, and other interactive elements.
- Real-Time Feedback:Interactive content provides immediate feedback on learner performance, allowing them to identify areas for improvement and adjust their learning approach.
- Personalized Learning:Interactive content can be tailored to individual learning styles and needs, providing a more personalized learning experience.
- Engaging and Motivating:Interactive elements such as games, simulations, and quizzes can make learning more enjoyable and motivating, leading to increased engagement and retention.
Examples of Interactive Content Formats
Various interactive content formats are commonly used in training programs. These formats cater to different learning styles and objectives:
- Interactive Videos:Videos with embedded quizzes, polls, and clickable elements allow learners to test their understanding and engage with the content.
- Simulations:Virtual environments that mimic real-world scenarios provide hands-on experience and allow learners to practice skills in a safe and controlled setting.
- Games:Gamified learning experiences make training fun and engaging while reinforcing key concepts and skills.
- Interactive Quizzes and Assessments:These allow learners to test their knowledge and receive immediate feedback, identifying areas for further study.
- Interactive Worksheets and Activities:These provide opportunities for learners to apply concepts and skills learned in a practical way.
Effectiveness of Interactive Content
Interactive content offers several advantages over traditional training methods, leading to improved learning outcomes:
- Increased Engagement and Retention:Interactive elements make learning more engaging and enjoyable, leading to improved retention of information.
- Enhanced Skill Development:Interactive content provides opportunities for hands-on practice and skill development, leading to improved competency.
- Personalized Learning Experience:Interactive content can be tailored to individual needs and learning styles, leading to more effective learning.
- Real-Time Feedback and Assessment:Interactive content provides immediate feedback on learner performance, allowing for timely adjustments and improvement.
Types of Interactive Content: Interactive Content For Training
Interactive content is a powerful tool for engaging learners and enhancing the effectiveness of training programs. It allows participants to actively participate in the learning process, making it more memorable and enjoyable.
Types of Interactive Content
Interactive content can be categorized into various types, each offering unique benefits and engaging learners in different ways.
| Content Type | Description | Benefits | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Quizzes and Assessments | These assess learners’ understanding of the material by presenting questions in various formats, such as multiple-choice, true/false, fill-in-the-blank, or open-ended questions. |
|
|
| Simulations and Games | These provide learners with a safe and controlled environment to practice skills or make decisions in a real-world context. They often involve scenarios, challenges, and feedback mechanisms. |
|
|
| Interactive Videos | These enhance traditional videos by incorporating interactive elements, such as quizzes, polls, branching scenarios, and clickable hotspots. |
|
|
| Interactive Infographics | These visually represent complex information in an engaging and easily digestible format. They often include interactive elements, such as clickable charts, data visualizations, and animations. |
|
|
Benefits of Interactive Content for Training
Interactive content in training offers a dynamic and engaging learning experience, significantly enhancing the effectiveness of knowledge acquisition and skill development. By actively involving learners, interactive content fosters deeper understanding, improved retention, and enhanced motivation.
Learner Engagement
Interactive content significantly enhances learner engagement by transforming passive learning into an active and participatory experience. This approach keeps learners actively involved in the learning process, promoting higher levels of focus and attention.
- Gamification:Incorporating game mechanics like points, badges, and leaderboards creates a sense of competition and accomplishment, encouraging learners to actively participate and strive for better performance.
- Interactive Exercises:Activities like quizzes, simulations, and interactive scenarios require learners to apply their knowledge and skills in real-time, making the learning process more engaging and memorable.
- Personalized Learning:Interactive content can adapt to individual learning styles and preferences, providing learners with a customized learning experience that caters to their specific needs and interests.
Knowledge Retention and Skill Application
Interactive content promotes deeper understanding and knowledge retention by encouraging learners to actively engage with the material and apply their knowledge in practical settings.
- Active Recall:Interactive exercises and assessments require learners to actively recall information, strengthening their understanding and memory retention.
- Practical Application:Simulations, role-playing scenarios, and interactive case studies provide learners with opportunities to apply their knowledge and skills in real-world contexts, enhancing their ability to transfer learning to practical situations.
- Feedback and Reinforcement:Immediate feedback on interactive exercises and assessments helps learners identify areas for improvement and reinforces their understanding of the concepts.
Learner Satisfaction and Motivation
Interactive content significantly improves learner satisfaction and motivation by creating a more engaging and enjoyable learning experience.
- Increased Enjoyment:Interactive content makes learning more enjoyable and engaging, reducing the perception of training as a tedious or passive activity.
- Sense of Accomplishment:Interactive exercises and assessments provide learners with a sense of accomplishment and progress, motivating them to continue learning.
- Increased Confidence:Interactive content allows learners to practice and apply their knowledge in a safe and supportive environment, boosting their confidence and motivation.
Designing Interactive Content
Creating engaging and effective interactive content for training requires careful planning and design. It involves understanding the target audience, the learning objectives, and the most suitable interactive formats.
Key Considerations for Designing Interactive Content
Designing interactive content for training involves several key considerations:
- Learning Objectives:Clearly define the learning objectives to ensure that the interactive content aligns with the desired outcomes. The content should be designed to facilitate the achievement of these objectives.
- Target Audience:Understand the target audience’s prior knowledge, skills, and learning preferences. Tailor the interactive content to their needs and interests to maximize engagement.
- Content Structure and Flow:Create a logical and engaging flow for the interactive content. Break down complex information into smaller, digestible chunks, and use clear transitions between sections.
- Interactive Elements:Choose interactive elements that are appropriate for the learning objectives and target audience. For example, quizzes, simulations, games, and interactive videos can be effective tools for enhancing engagement and knowledge retention.
- Accessibility:Ensure that the interactive content is accessible to all learners, including those with disabilities. Use clear and concise language, provide alternative text for images, and consider the needs of learners with visual or auditory impairments.
- Feedback and Assessment:Provide immediate feedback to learners, allowing them to track their progress and identify areas for improvement. Include assessments to measure learning outcomes and provide insights for future training development.
Evaluating the Effectiveness of Interactive Content
To ensure the effectiveness of interactive content, it is crucial to evaluate its impact on learning outcomes. Here’s a checklist for evaluating the effectiveness:
- Engagement:Does the interactive content hold learners’ attention and encourage active participation? Observe learner engagement metrics such as time spent on the content, completion rates, and interaction frequency.
- Learning Outcomes:Does the interactive content contribute to the achievement of the desired learning objectives? Assess learner knowledge and skills through pre- and post-training assessments, surveys, or performance evaluations.
- Feedback:Gather feedback from learners on their experience with the interactive content. Ask for their opinions on the effectiveness, clarity, and engagement level of the content.
- Data Analysis:Analyze the data collected from engagement metrics, assessments, and feedback to identify areas for improvement and refine the interactive content for future iterations.
Selecting Appropriate Interactive Content Formats
The choice of interactive content format depends on the training objectives, target audience, and available resources. Here are some guidelines for selecting appropriate formats:
- Interactive Videos:Effective for delivering information, demonstrating procedures, and providing visual explanations. Interactive elements can include quizzes, polls, and branching scenarios to enhance engagement and knowledge retention.
- Simulations:Ideal for providing hands-on experience in a safe and controlled environment. Simulations can be used to practice skills, test theories, and explore different scenarios.
- Games:Gamification can be a powerful tool for engaging learners and making training fun. Games can be used to reinforce concepts, develop problem-solving skills, and promote collaboration.
- Quizzes and Assessments:Useful for evaluating learner understanding and identifying knowledge gaps. Quizzes can be used to reinforce learning, provide feedback, and track progress.
- Interactive Infographics:A visually appealing way to present data, concepts, and processes. Interactive infographics can include clickable elements, animations, and interactive charts to enhance understanding and engagement.
Interactive Content for Different Learning Styles
Interactive content can be a valuable tool for training because it caters to various learning styles. By providing different formats and approaches, interactive content can make learning more engaging and effective for a wider range of individuals.
Learning Styles and Interactive Content Formats
Understanding how different learning styles interact with interactive content formats can help you design more effective training materials. Here is a table summarizing the relationship between learning styles and content formats:
| Learning Style | Interactive Content Formats | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Visual | Infographics, Videos, Interactive Diagrams, Simulations | An interactive infographic that allows learners to explore the different stages of a process. A video tutorial demonstrating how to use a new software program. An interactive diagram that lets learners manipulate the components of a machine. A simulation that allows learners to experience a real-world scenario, such as responding to a customer complaint. |
| Auditory | Audio Narrations, Podcasts, Interactive Transcripts, Games with Sound Effects | An audio narration that explains a complex concept. A podcast featuring interviews with experts in the field. An interactive transcript that allows learners to listen to and read the text simultaneously. A game that uses sound effects to provide feedback and reinforce learning. |
| Kinesthetic | Interactive Games, Simulations, Role-Playing Activities, Virtual Reality Experiences | An interactive game that challenges learners to apply their knowledge in a fun and engaging way. A simulation that allows learners to practice skills in a safe and controlled environment. A role-playing activity that encourages learners to put themselves in the shoes of others. A virtual reality experience that immerses learners in a realistic environment. |
Integrating Interactive Content into Training Programs
Interactive content can significantly enhance the effectiveness of training programs. It offers engaging and interactive learning experiences, leading to improved knowledge retention and application. Integrating interactive content requires a strategic approach to ensure it complements existing training materials and enhances the overall learning experience.
Strategies for Seamless Integration
Integrating interactive content into existing training programs involves considering the program’s goals, target audience, and existing resources. Here are some strategies to ensure a smooth transition:
- Start Small:Begin by introducing interactive elements gradually into existing training modules. This allows for testing and refining the approach before implementing it on a larger scale.
- Align with Learning Objectives:Ensure that interactive content aligns with the specific learning objectives of each training module. This ensures that the content is relevant and contributes to the overall learning goals.
- Utilize Existing Resources:Explore opportunities to repurpose existing training materials into interactive formats. This can be done by converting presentations into interactive quizzes or incorporating video clips into simulations.
- Leverage Technology:Utilize learning management systems (LMS) or other online platforms to deliver and track interactive content. This provides a centralized location for accessing and managing training materials.
Developing and Implementing Interactive Content
Developing and implementing interactive content involves a systematic process. The following flowchart illustrates the key steps involved:[Flowchart: Start with a “Define Objectives” box. Branch out to “Choose Interactive Content Type” (e.g., quizzes, simulations, games) and “Identify Target Audience.” These branches then converge into “Design Interactive Content.” This leads to “Pilot Testing” and then “Implement and Evaluate.” Finally, the process can loop back to “Define Objectives” for ongoing improvement.]
Interactive content can be a powerful tool for training, allowing learners to actively engage with the material and receive immediate feedback. To ensure your training program is effective, it’s essential to measure its success. Just as you would track the results of a video marketing campaign, How to measure the success of video marketing campaigns offers valuable insights on how to track engagement, completion rates, and knowledge retention within your training program.
By analyzing these metrics, you can identify areas for improvement and ensure your interactive content delivers the desired learning outcomes.
Potential Challenges and Solutions
Integrating interactive content can present challenges, but with proper planning and implementation, these obstacles can be overcome.
- Resistance to Change:Some learners may be resistant to new learning methods. Addressing this requires clear communication about the benefits of interactive content and providing adequate support and training.
- Time and Resource Constraints:Developing and implementing interactive content can be time-consuming and require resources. Prioritizing content development, leveraging existing resources, and seeking external support can help mitigate these challenges.
- Technical Difficulties:Technical issues can arise with the delivery and accessibility of interactive content. Ensuring compatibility across different devices and platforms, providing technical support, and conducting thorough testing can address these concerns.
Evaluating Interactive Content Effectiveness
Evaluating the effectiveness of interactive content in training programs is crucial for ensuring that learning objectives are met and that the content is engaging and impactful. By measuring the success of interactive content, you can identify areas for improvement and optimize the learning experience for participants.
Interactive content for training is a powerful tool for engaging learners and improving knowledge retention. It can be particularly effective when paired with video marketing techniques, which can help to bring the content to life and make it more relatable.
To learn more about how video marketing can enhance customer engagement, check out this helpful article: Using video marketing to improve customer engagement. By incorporating engaging video elements, interactive training content can create a truly immersive and memorable learning experience.
Methods for Evaluating Interactive Content Effectiveness
Several methods can be used to assess the effectiveness of interactive content in training programs. These methods provide valuable insights into the impact of the content on learner engagement, knowledge acquisition, and performance.
| Evaluation Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Pre- and Post-Tests | These tests measure knowledge acquisition before and after engaging with the interactive content. They help determine if learners have gained new knowledge or skills through the training. |
| Performance-Based Assessments | These assessments evaluate learners’ ability to apply the knowledge and skills learned from the interactive content in real-world scenarios. They can include simulations, case studies, or practical exercises. |
| Engagement Metrics | These metrics track learner interaction with the interactive content, such as time spent on specific modules, completion rates, and the number of attempts required to complete tasks. |
| Surveys and Feedback Forms | Collecting learner feedback through surveys and forms provides valuable insights into their satisfaction with the interactive content, their perceived learning outcomes, and areas for improvement. |
| Focus Groups and Interviews | These qualitative methods allow for in-depth discussions with learners to gather detailed insights into their experiences with the interactive content, their perceptions of its effectiveness, and any challenges they faced. |
Collecting and Using Learner Feedback
Collecting learner feedback is essential for improving interactive content. Feedback can provide valuable insights into the strengths and weaknesses of the content, identify areas that need improvement, and ensure that the content remains relevant and engaging for learners.
“By actively seeking and incorporating learner feedback, you can create interactive content that is tailored to the specific needs and preferences of your audience.”
There are several ways to collect learner feedback, including:
- Post-Training Surveys: These surveys can be used to gather feedback on the overall effectiveness of the interactive content, specific modules, and the learning experience.
- Focus Groups: Focus groups provide a platform for learners to discuss their experiences with the interactive content in a group setting, allowing for a more in-depth understanding of their perspectives.
- Individual Interviews: One-on-one interviews with learners allow for personalized feedback and a deeper understanding of their individual experiences with the interactive content.
Using learner feedback effectively requires careful analysis and interpretation. The feedback should be reviewed to identify common themes, patterns, and areas for improvement. This information can then be used to revise and enhance the interactive content, making it more effective and engaging for future learners.
Interactive Content for Different Training Contexts
Interactive content can be effectively employed across various training contexts, each with its unique characteristics and needs. It enhances engagement, promotes active learning, and adapts to different learning styles and environments.
Interactive Content in Corporate Training, Interactive content for training
Interactive content plays a crucial role in corporate training by providing engaging and effective learning experiences. It caters to the specific needs of employees, ensuring they acquire the necessary skills and knowledge to excel in their roles.
- Onboarding:Interactive modules can introduce new employees to company culture, policies, and procedures in an engaging manner. Gamified onboarding programs can help employees quickly grasp essential information and build a sense of belonging.
- Product Training:Interactive simulations and virtual reality experiences allow employees to learn about products and services in a hands-on way. This fosters a deeper understanding of product features and benefits, leading to improved sales and customer service.
- Compliance Training:Interactive content can make compliance training more engaging and effective. Interactive scenarios and quizzes can help employees understand and retain crucial compliance information, reducing the risk of errors and violations.
- Leadership Development:Interactive content can facilitate leadership development by providing opportunities for employees to practice their leadership skills in safe and controlled environments. Role-playing scenarios, simulations, and interactive case studies allow participants to develop critical thinking, decision-making, and communication skills.
Interactive Content in Educational Training
Interactive content is transforming the educational landscape by providing students with more engaging and personalized learning experiences. It caters to different learning styles and allows for active participation, making learning more effective and enjoyable.
Interactive content for training is becoming increasingly popular as it offers a more engaging and effective learning experience. This approach aligns with the growing trend of voice search optimization, which is transforming how people interact with information. As we move towards a future where voice search dominates, The future of voice search optimization will be crucial for making training materials accessible and easily discoverable.
Interactive content, with its natural conversational style, is well-suited to this evolving landscape, offering a seamless bridge between learning and voice-driven information retrieval.
- K-12 Education:Interactive games, quizzes, and simulations can make learning fun and engaging for students of all ages. Interactive content can be used to teach subjects like math, science, history, and language arts in a more engaging and effective way.
- Higher Education:Interactive content can be used to enhance lectures, facilitate group discussions, and provide students with personalized learning experiences. Interactive case studies, simulations, and virtual labs allow students to apply their knowledge in real-world scenarios.
- Online Learning:Interactive content is essential for online learning, providing a sense of interactivity and engagement. Interactive quizzes, forums, and collaborative projects foster a sense of community and encourage active participation among online learners.
Interactive Content in Professional Development
Interactive content is a valuable tool for professional development, providing individuals with opportunities to learn new skills, expand their knowledge, and stay ahead of industry trends.
- Skill-Building:Interactive content can help professionals develop new skills in areas like technology, communication, and leadership. Interactive tutorials, simulations, and case studies provide hands-on learning experiences that accelerate skill development.
- Continuing Education:Interactive content makes continuing education more accessible and engaging for busy professionals. Interactive courses and webinars allow individuals to learn at their own pace and in a way that fits their busy schedules.
- Career Advancement:Interactive content can help professionals prepare for career advancement by providing them with the knowledge and skills they need to succeed in new roles. Interactive assessments and simulations can help individuals identify their strengths and weaknesses, allowing them to focus on areas where they need to improve.
Interactive content can be a powerful tool for training, allowing learners to engage with material in a dynamic and memorable way. This approach is particularly relevant for e-commerce businesses, as they can leverage interactive content to educate customers about products and services.
For instance, video tutorials, a key element of video marketing for e-commerce businesses , can effectively guide customers through product features and demonstrate usage scenarios. By integrating interactive elements into training materials, businesses can enhance engagement, boost knowledge retention, and ultimately improve customer satisfaction.
Interactive Content in Online and Offline Training Environments
Interactive content can be effectively used in both online and offline training environments, offering unique advantages in each setting.
- Online Training:Interactive content is particularly well-suited for online training, as it can provide a sense of interactivity and engagement that is often lacking in traditional online courses. Interactive quizzes, games, and simulations can help learners stay focused and motivated, while online forums and collaborative projects can foster a sense of community among learners.
- Offline Training:Interactive content can also be used in offline training environments, such as workshops, seminars, and conferences. Interactive exercises, group activities, and simulations can help learners engage with the material and apply their knowledge in real-world scenarios.
Future Trends in Interactive Content for Training
The landscape of training is rapidly evolving, driven by advancements in technology and changing learning preferences. Interactive content is at the forefront of this transformation, with emerging trends promising to revolutionize the way we learn and train.
Gamification
Gamification involves incorporating game-like elements into training programs to enhance engagement and motivation. This approach leverages the principles of game design, such as points, badges, leaderboards, and challenges, to create a more enjoyable and rewarding learning experience.
- Increased Engagement:Gamification taps into our innate desire for competition and achievement, making learning more engaging and motivating. By incorporating game mechanics, training programs can capture attention and encourage active participation, leading to improved knowledge retention and skill development.
- Personalized Learning:Gamified training can be tailored to individual learning styles and preferences. For example, learners can choose their own paths, compete against themselves or others, and receive personalized feedback based on their performance. This personalized approach fosters a sense of ownership and encourages learners to take charge of their learning journey.
Interactive content can be a powerful tool for training, engaging learners and fostering knowledge retention. One effective way to enhance this engagement is by incorporating video, a medium that can captivate audiences and convey information in a dynamic and memorable way.
To learn more about how video can be used to drive sales, explore this informative resource: How to use video marketing to drive sales. Applying the principles of effective video marketing can be seamlessly integrated into training programs, ensuring that content is not only informative but also engaging and impactful.
- Data-Driven Insights:Gamified training platforms collect data on learner progress, engagement levels, and performance metrics. This data provides valuable insights into learner behavior, allowing training professionals to identify areas for improvement and optimize the learning experience.
Virtual Reality (VR)
Virtual reality (VR) immerses learners in simulated environments, providing realistic and engaging training experiences. VR technologies create immersive 3D worlds that allow learners to interact with virtual objects and environments, fostering deeper understanding and skill development.
- Realistic Simulations:VR allows for the creation of realistic simulations of real-world scenarios, providing learners with hands-on experience in a safe and controlled environment. This approach is particularly effective for training in high-risk industries such as healthcare, manufacturing, and aviation, where traditional methods may not be feasible or safe.
- Enhanced Learning Outcomes:By providing immersive and interactive experiences, VR can improve learning outcomes by increasing knowledge retention, skill proficiency, and problem-solving abilities. VR training programs can also provide immediate feedback and guidance, allowing learners to learn from their mistakes in a safe and controlled environment.
- Cost-Effective Training:VR training can be more cost-effective than traditional methods, particularly for scenarios that require expensive or dangerous equipment or environments. VR training eliminates the need for physical training facilities and equipment, reducing costs associated with travel, logistics, and safety measures.
Augmented Reality (AR)
Augmented reality (AR) overlays digital information onto the real world, enhancing the learning experience by providing context and interactivity. AR technologies use cameras and sensors to create interactive experiences that blend digital content with the real world, enabling learners to engage with their surroundings in new and innovative ways.
- Hands-On Learning:AR provides hands-on learning experiences by allowing learners to interact with digital objects and information in their real-world environment. This approach is particularly effective for training in fields such as engineering, construction, and healthcare, where learners need to apply their knowledge in practical settings.
- Improved Information Retention:AR can enhance information retention by providing context and interactivity. By overlaying digital information onto the real world, AR training programs can help learners connect abstract concepts with real-world applications, leading to deeper understanding and improved recall.
- Increased Accessibility:AR training programs can be accessed anytime, anywhere, using mobile devices or wearable technologies. This accessibility makes AR a valuable tool for training employees in remote locations or for providing on-demand training resources.
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Artificial intelligence (AI) is transforming the way we learn and train, providing personalized learning experiences, intelligent feedback, and automated assessments. AI-powered training platforms can analyze learner data to identify strengths and weaknesses, provide tailored recommendations, and adapt to individual learning needs.
- Personalized Learning Paths:AI-powered training platforms can create personalized learning paths based on learner preferences, skill levels, and learning goals. This personalized approach ensures that learners receive the most relevant and effective training content, maximizing their learning outcomes.
- Intelligent Feedback and Guidance:AI algorithms can provide learners with real-time feedback and guidance, helping them to identify areas for improvement and adjust their learning strategies. This personalized feedback can accelerate learning and enhance knowledge retention.
- Automated Assessments and Evaluation:AI can automate assessments and evaluations, freeing up training professionals to focus on other tasks. AI-powered assessment tools can provide accurate and objective feedback, ensuring fair and consistent evaluation of learner progress.
Closing Summary
Interactive content for training is more than just a trend; it’s a transformative approach that’s here to stay. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect even more innovative and engaging ways to learn. By embracing interactive content, we empower learners to take control of their education, fostering a more dynamic and fulfilling learning journey.
Query Resolution
What are some examples of interactive content for training?
Interactive content encompasses a wide range of formats, including quizzes, simulations, games, interactive videos, virtual reality experiences, and more. The specific format chosen will depend on the training objectives and learning styles of the participants.
How can I measure the effectiveness of interactive content?
You can assess the effectiveness of interactive content by tracking learner engagement, knowledge retention, and skill application. Collecting feedback through surveys, quizzes, and performance assessments can provide valuable insights into the impact of interactive content on learning outcomes.